코딩테스트(Javascript)
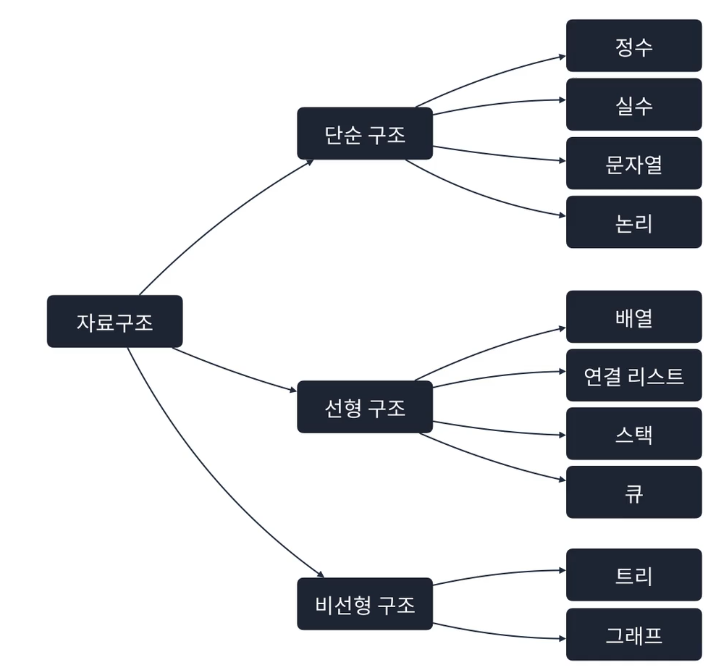
자료구조와 알고리즘
자료구조와 알고리즘의 중요성
- 요리에 빗대서
- 재료 : data
- 도구 : 자료구조
- 레시피 : 알고리즘
- 자료구조 + 알고리즘 : 프로그램
자료구조
- 메모리를 효율적으로 사용하며 빠르고 안정적으로 데이터처리
- Stack
- Queue
- Graph
- Tree
알고리즘
- 특정 문제를 효율적이고 빠르게 해결하는 것이 궁극적인 목표
- Binary Search
- Shortest Path
코딩테스트 준비
문제를 풀때
- 여러가지 풀이 방법이 있을 수 있다는 것
- 예외가 있을 수 있다는 것
- 정답이 베스트인지
- 시행착오 모두 기록
- 다른 사람의 코드 많이 보기
- 쉽게 포기하지 않되, 답을 적절히 활용
익숙해지기
- 시간복잡도 계산 익숙해져야됨
- 엣지 케이스 생각에 익숙
좋은 코드 만들기
- 간결하고 가독성 좋은 코드
- 변수명, 함수형
- 중복코드 제거
- map, filter, reduce 등 활용
- 가지치기 활용
- 자바스크립트 문법 잘 활용
- 일관성을 잘 유지했는가
자료구조
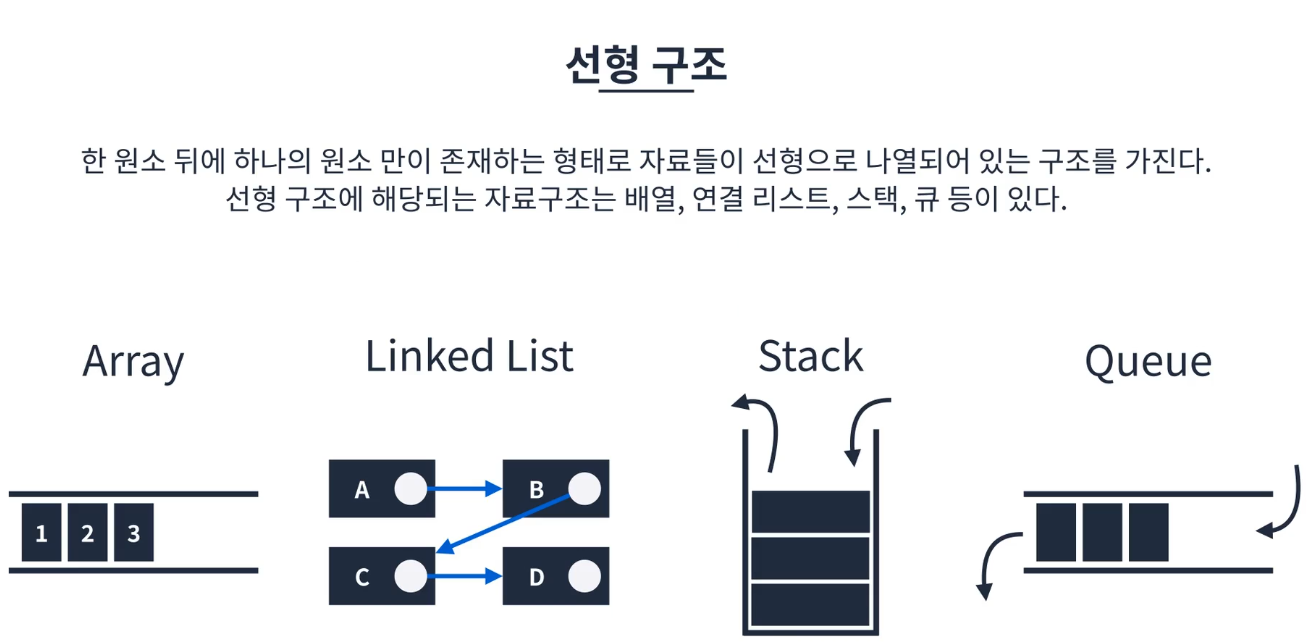
선형구조
- 한 원소 뒤에 하나의 원소만 존재하는 형태
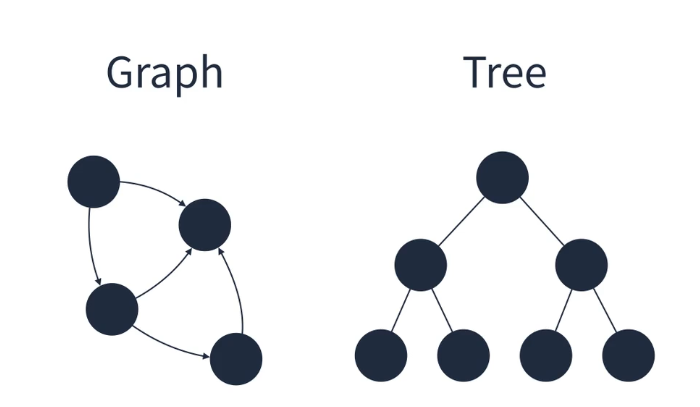
비선형구조
- 계층적 구조나 망형 구조표현에 적절
시간복잡도
- BigO 표기법 # 노마크코더 설명
자바스크립트 코드 트릭
1 구조분해할당을 이용한 변수 swap
1
2
3
let a = 5, b = 10;
[a, b] = [b, a];
console.log(a, b); // 10 5
2 배열 생성으로 루프 제거
범위 루프
1
2
3
4
let sum = 0;
for (let i = 5; i < 10; i += 1) {
sum += i;
}
함수형 범위루프
1
2
3
const sum = Array
.from(new Array(5), (_, k) => k + 5)
.reduce((acc, cur) => acc + cur, 0);
3 배열 내 같은 요소 제거
1
2
3
const names = ['Lee', 'Kim', 'Park', 'Lee', 'Kim'];
const uniqueNamesWithArrayFrom = Array.from(new Set(names));
const uniqueNamesWithSpread = [...new Set(names)];
4 Spread 연산자를 이용한 객체 병합
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
const person = {
name: 'Lee Sun-Hyoup',
familyName: 'Lee',
givenName: 'Sun-Hyoup'
};
const company = {
name: 'Cobalt. Inc.',
address: 'Seoul'
};
const leeSunHyoup = { ...person, ...company };
console.log(leeSunHyoup);
5 &&와 || 활용
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
/// ||
// 기본값을 넣어주고 싶을 때 사용할 수 있습니다.
// participantName이 0, undefined, 빈 문자열, null일 경우 'Guest'로 할당됩니다.
const name = participantName || 'Guest';
/// &&
// flag가 true일 경우에만 실행됩니다.
flag && func();
// 객체 병합에도 이용할 수 있습니다.
const makeCompany = (showAddress) => {
return {
name: 'Cobalt. Inc.',
...showAddress && { address: 'Seoul' }
}
};
console.log(makeCompany(false));
// { name: 'Cobalt. Inc.' }
console.log(makeCompany(true));
// { name: 'Cobalt. Inc.', address: 'Seoul' }
6 구조 분해 할당 사용하기
- 객체에서 필요한것만 꺼내씀
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
const person = {
name: 'Lee Sun-Hyoup',
familyName: 'Lee',
givenName: 'Sun-Hyoup',
company: 'Cobalt. Inc.',
address: 'Seoul'
}
const { familyName, givenName } = person;
7 객체 생성시 키 생략
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
const name = 'Lee Sun-Hyoup';
const company = 'Cobalt';
const person = {
name,
company
}
console.log(person);
// {
// name: 'Lee Sun-Hyoup'
// company: 'Cobalt',
// }
8 비구조화 할당 사용
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
const makeCompany = ({ name, address, serviceName }) => {
return {
name,
address,
serviceName
}
};
const cobalt = makeCompany({ name: 'Cobalt. Inc.', address: 'Seoul', serviceName: 'Present' });
9 동적 속성 이름
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
const nameKey = 'name';
const emailKey = 'email';
const person = {
[nameKey]: 'Lee Sun-Hyoup',
[emailKey]: 'kciter@naver.com'
};
console.log(person);
// {
// name: 'Lee Sun-Hyoup',
// email: 'kciter@naver.com'
// }
10 !! 연산자를 사용하여 Boolean 값으로 바꾸기
- !! 연산자를 이용하여 0, null, 빈 문자열, undefined, NaN을 false로 그 외에는 true로 변경할 수 있습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
function check(variable) {
if (!!variable) {
console.log(variable);
} else {
console.log('잘못된 값');
}
}
check(null); // 잘못된 값
check(3.14); // 3.14
check(undefined); // 잘못된 값
check(0); // 잘못된 값
check('Good'); // Good
check(''); // 잘못된 값
check(NaN); // 잘못된 값
check(5); // 5
11 sort
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
// 오름차순 정렬
const numbers = [3, 1, 4, 1, 5, 9, 2, 6, 5, 3, 5];
numbers.sort((a, b) => a - b);
console.log(numbers); // [1, 1, 2, 3, 3, 4, 5, 5, 5, 6, 9]
// 내림차순 정렬
numbers.sort((a, b) => b - a);
console.log(numbers); // [9, 6, 5, 5, 5, 4, 3, 3, 2, 1, 1]
배열(순차 리스트)
- 연관된 데이터를 연속적인 형태로 구성된 구조로, 배열에 포함된 원소는 순서대로 Index가 붙는다.
- 고정된 크기를 가지며 일반적으로 동적으로 크기를 늘릴 수 없음
- 원하는 원소의 index를 알고 있으면 해당 데이터를 찾을 수 있고, 삭제하면 빈자리가 생긴다.
배열 생성

배열 요소 추가 및 삭제

배열과 객체
- length()를 통해 배열 길이를 알 수 있음.
- join(“, “)을 통해 배열 값을 모두 String으로 합칠 수 있음
- reverse()를 통해 함수값들이 전부 뒤집어짐.
- arr1.concat(arr2) 를 통해 배열을 합칠 수 있음.
- push() : 배열 끝에 요소 추가
- pop() : 배열 끝 요소 삭제
- shift() : 맨 앞 요소 삭제
- unshift() : 맨 앞 요소 추가
- slice(startIndex, endIndex) : 중간 요소들을 자름. 원본 배열이 변화되지 않음.
- splice(startIndex, count) : startIndex부터 count까지 삭제
- 배열의 반복문
1
2
3
for (const item of arr) {
console.log(item);
}
객체 생성
- new Object(); or {};
- ‘email’ in obj : 실제로 키가 있는지 없는지 확인하는 방법
- Object.keys(obj) : 배열의 형태로 객체의 key 목록을 얻을 수 있음
- Object.values(obj) : 배열의 형태로 객체의 value 목록을 얻을 수 있음
- 객체의 반복문
1
2
3
for (const key in obj) {
console.log(key, obj[key]);
}
연결리스트
- 요소 추가와 삭제가 반복되는 로직이라면?? 배열은 탐색이 많은 경우 유리.
- Singly Linked List
- Doubly Linked List
- Circular Linked List
배열과의 차이점
- 메모리 차이
단일연결리스트(Singly Linked List)
- Head에서 Tail까지 단방향으로 이어지는 단순한 연결 리스트
요소 찾기
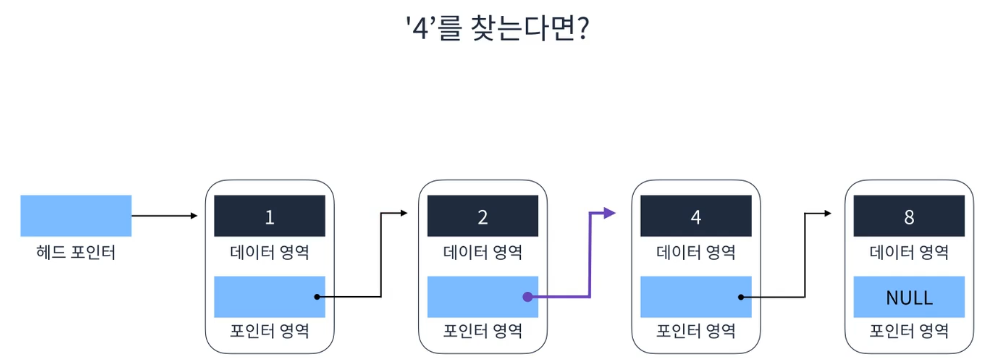
요소 추가
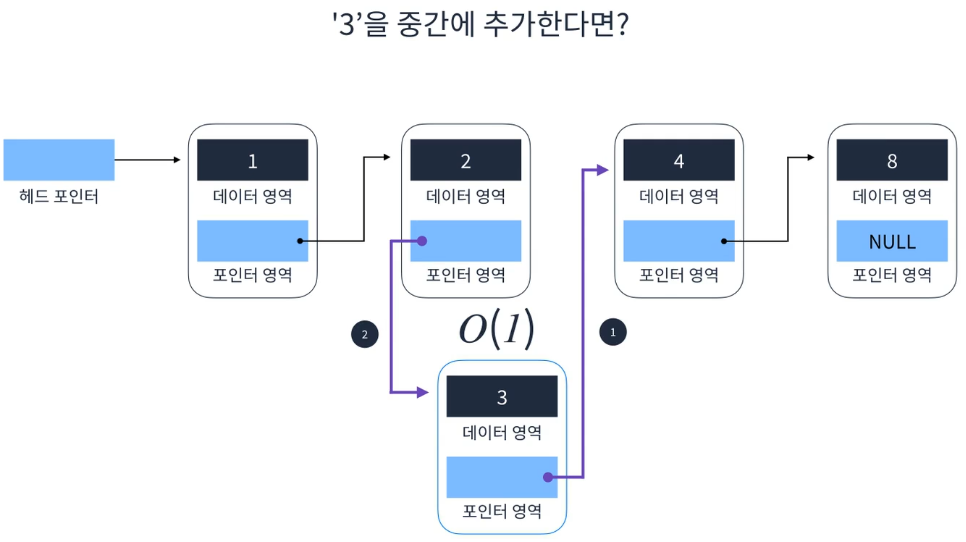
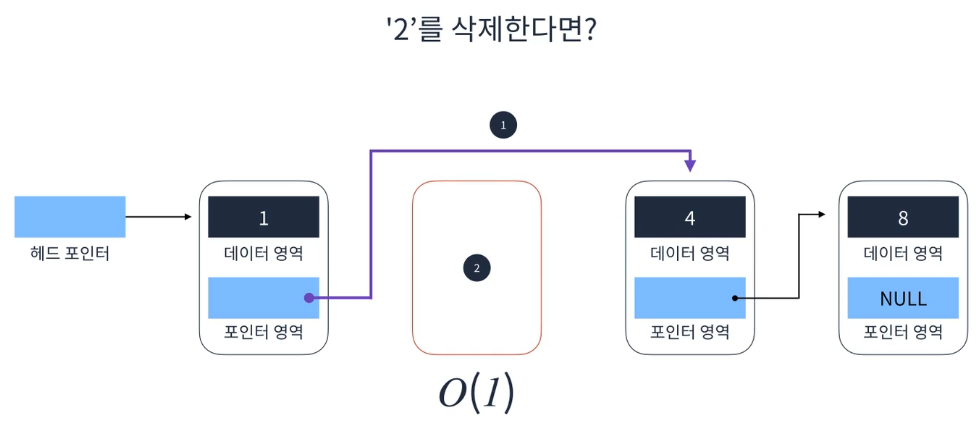
요소 삭제
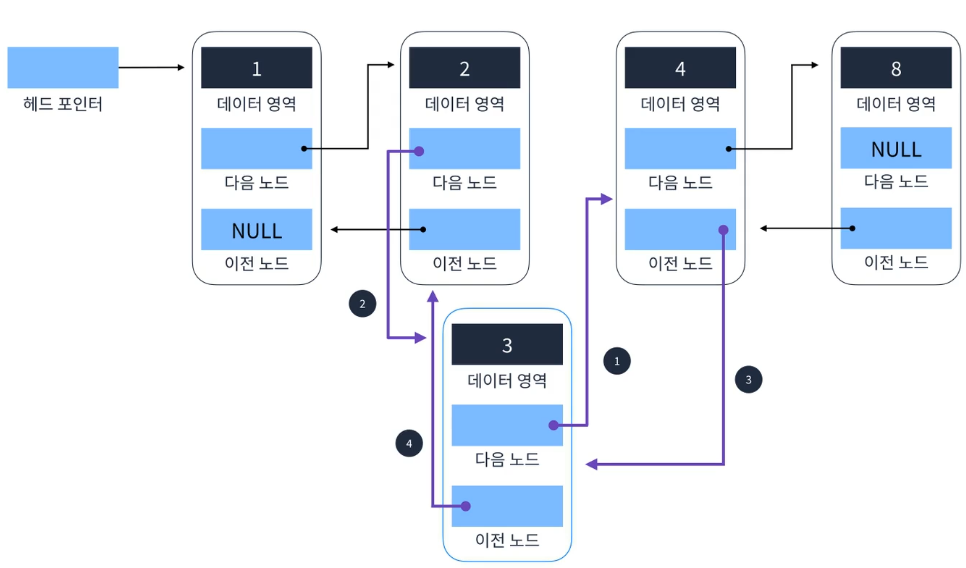
이중연결리스트(Doubly Linked List)
- 이전노드 다음노드에 대한 Pointer 2개 존재하므로 자료구조의 크기가 조금 더 크다
요소 추가
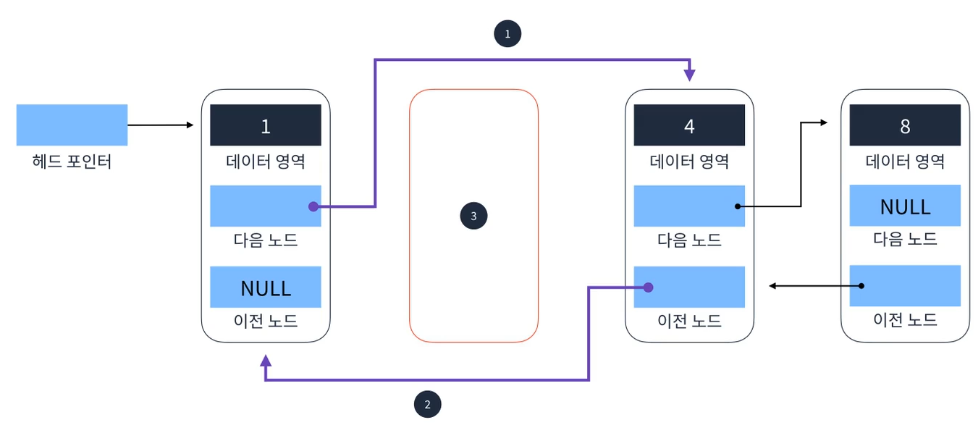
요소 삭제
환영연결리스트(Circular Linked List)
- Singly 또는 Doubly에서 Tail이 Head로 연결되는 연결 리스트
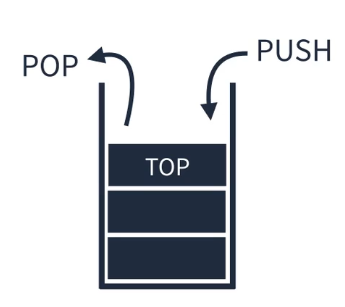
Stack
- Last In First Out이라는 개념을 가진 선형 자료구조
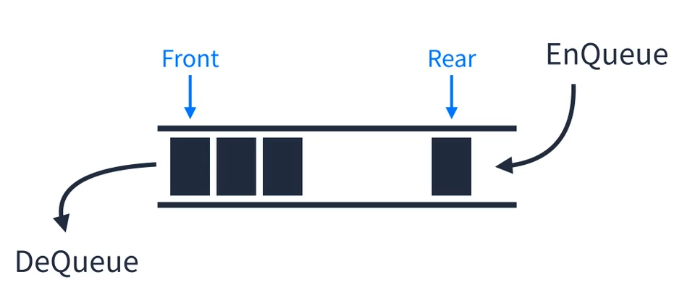
큐
- First In First Out이라는 개념을 가진 선형 자료구조
Array로 구현
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
class Queue {
constructor() {
this.queue = [];
this.front = 0;
this.rear = 0;
}
enqueue(value) {
this.queue[this.rear++] = value;
}
dequeue() {
const value = this.queue[this.front];
delete this.queue[this.front];
this.front += 1;
return value;
}
// Queue 의 가장 앞에 있는 값을 알아내는 함수
peek(){
return this.queue[this.front];
}
// 크기 알아내는 함수
size() {
return this.rear - this.front;
}
}
Linked List로 구현
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.next = null;
}
}
class Queue {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this.size = 0;
}
enqueue(newValue) {
const newNode = new Node(newValue);
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = this.tail = newNode;
}
else {
this.tail.next = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
}
this.size += 1;
}
dequeue() {
const value = this.head.value;
this.head = this.head.next;
this.size -= 1;
return value;
}
peek(){
return this.head.value;
}
}
Circular Queue : 환영큐
배열로 구현
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
class Queue {
constructor(maxSize) {
this.maxSize = maxSize;
this.queue = [];
this.front = 0;
this.rear = 0;
this.size = 0;
}
enqueue(value) {
if (this.isFull()) {
console.log("Queue is full.");
return;
}
this.queue[this.rear] = value;
this.rear = (this.rear + 1) % this.maxSize;
this.size += 1;
}
dequeue() {
const value = this.queue[this.front];
delete this.queue[this.front];
this.front = (this.rear + 1) % this.maxSize;
this.size -= 1;
return value;
}
// Queue 의 가장 앞에 있는 값을 알아내는 함수
peek(){
return this.queue[this.front];
}
// 크기 알아내는 함수
isFull() {
return this.size === this.maxSize;
}
}
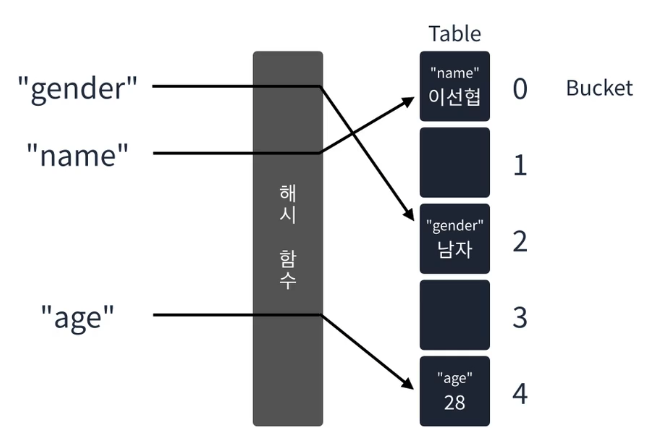
해시 테이블
- 키와 값을 받아 키를 해싱하여 나온 index에 값을 저장하는 선형 자료구조
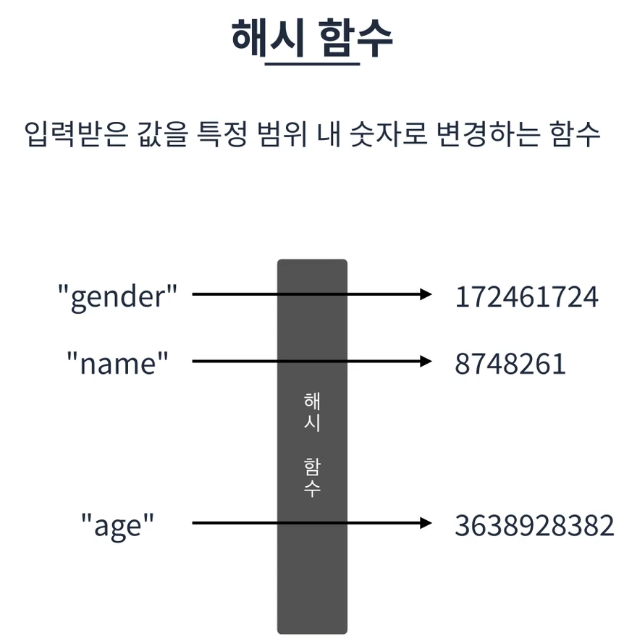
해시 함수
- 입력받은 값을 특정 범위 내 숫자로 변경하는 함수
해시 충돌(Hash Collision)
- 해결방법은 아래와 같다.
선형 탐사법
- 충돌이 발생하면 옆으로 한칸 이동한다.
제곱 탐사법
- 충돌이 발생하면 충돌이 발생한 횟수의 제곱만큼 옆으로 이동한다.
이중 해싱
- 충돌이 발생하면 다른 해시 함수를 이용한다.
분리 연결법
- 버킷의 값을 연결 리스트로 사용하여 충돌이 발생하면 리스트에 값을 축가한다.
Javascript에서 사용하는 방법
- 객체 이용
- Map Class 이용 : 배열이나 object도 key로 사용할 수 있음.
1
2
3
4
const table = new Map();
table.set("key", 100);
console.log(table["key"]);
console.log(table.get("key"));
- Set Class 이용 : Key와 Value가 동일하게 들어감
1
2
3
4
5
6
const table = new Set();
table.add("key");
table.add("key2");
table.has("key");
table.has("key2");
console.log(table.size);
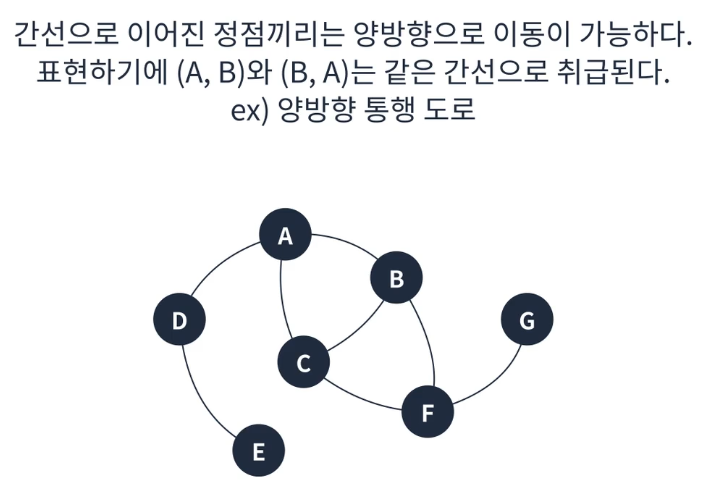
그래프
- 정점과 정점 사이를 연결하는 간선으로 이루어진 비선형 자료구조
- 정점은 여러개의 간선을 가질 수 있다.
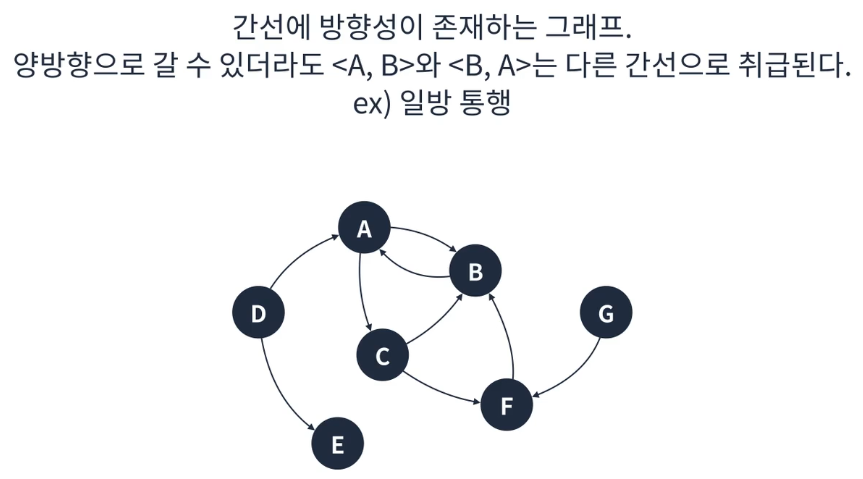
- 크게 방향 그래프와 무방향 그래프로 나눌 수 있다.
- 간선의 가중치를 가질 수 있다.
- 사이클이 발생할 수 있다.
무방향 그래프
방향 그래프
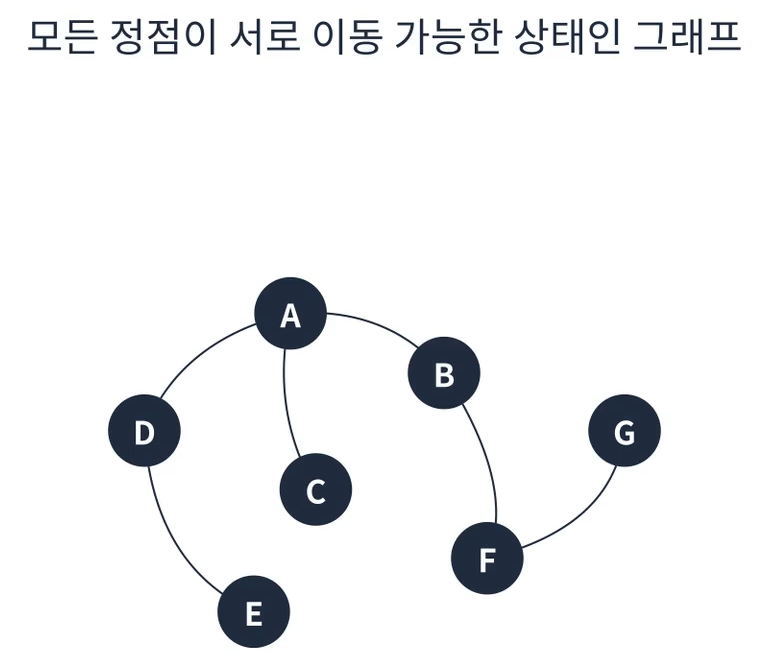
연결 그래프
댓글남기기